The tug Nellie Bly has completed the world’s first 1,000 nautical mile autonomous voyage marking a milestone in the use of computer vision and autonomous tech to circumnavigate Denmark and gather essential data on waterways. Using a system developed by Sea Machines Robotics of Boston, the voyage was completed in just 129 operational hours over 13 days. The program was commanded by U.S. Coast Guard-licensed mariners remotely stationed 3,000 miles away in Boston, many of whom are also members of the American Maritime Officers union.
“The completion of this voyage marks the catalyst for a new era of at-sea operations,” said Michael Johnson, CEO of Sea Machines. “Remotely commanded autonomous vessels provide the marine industries with the platform necessary to be competitive in the modern world, delivering significant increases in productivity and operational safety, digitized ultra-efficiency and response speed, and will provide a new world of actionable operational data for improved planning and business practices. The Machine Odyssey signals the start of a new human-technology relationship propelling on-sea operations in the 21st century.”
The Nellie Bly employed first-of-it’s-kind AI-enabled, long-range computer vision and a sensor-to-propeller autonomy system. Its technical features allowed for path-planning, active domain perception, dynamic obstacle, and traffic avoidance and replanning, depth sensing, and fusion of vectored nautical chart data. Sea Machines reports that 96.9 percent of the 1,027-mile journey was accomplished under fully autonomous control. During the voyage, they executed 31 collision avoidance and traffic separation maneuvers.

Nellie Bly navigated the waterways of Germany and Denmark commanded from Boston (Sea Machines)
The voyage began in Cuxhaven, Germany, and transited the Kiel Canal before traveling to the northernmost points of Denmark. The tug safely returned to Hamburg, Germany last week.
Using multi-sensor fusion, the system digitally perceived over 12,000 square miles of ocean space more accurately and comprehensively than comparable human operators. According to Sea Machines, this successful autonomous operation demonstrates that with this technology the world’s fleets can ply the oceans in a more predictable and safer manner, while optimizing the global supply chain by delivering a greatly more efficient and productive means of transportation than what exists today.
Throughout the voyage, the tug averaged a speed of 7.9 knots. Sea Machines garnered 3.8TB of essential operational data showcasing how the ships can readily connect as IOT systems into the cloud economy. The system also provided the remote commanders in Boston with an active chart of the environment and live augmented overlays showing the progress of the mission, state of the vessel, situational awareness of the domain, real-time vessel-borne audio, and video from many streaming cameras.
“Autonomy is taking hold faster on the waterways than it is on roadways,” said Johnson. “Our autonomous systems are already supporting vessel operations around the world in manned and unmanned capacities. We are rapidly retooling the marine industries with an advanced perception, self-piloting system, and connected vessel intelligence. The Machine Odyssey was a success and we believe we will soon see autonomy become commonplace.”
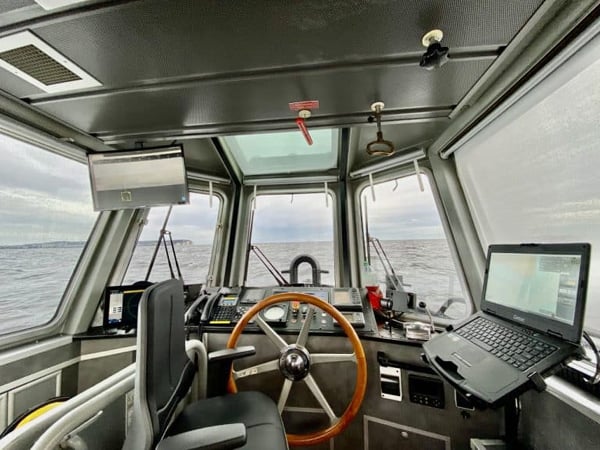

Pilot house of the Nellie Bly (Sea Machines)
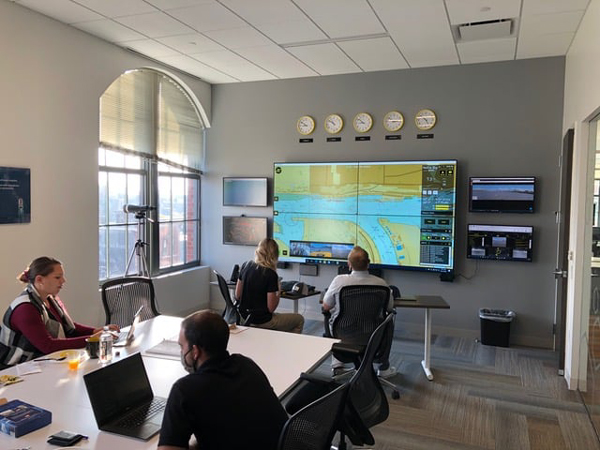
Team in Boston commanding the tug (Sea Machines)
Source: The Maritime Executive






